Diameter Copper Rod Is Reduced to a 387 Diameter Then Reduced Again to
Publist#: 144/8
Copper alloys become stronger and more ductile as temperature goes down. They also retain excellent impact resistance to 20 K. These general characteristics have been revealed in tests on 15 copper alloys, including brasses, bronzes and commercially pure coppers. They were tested by the Cryogenics Div., National Bureau of Standards, for the copper and brass industry to check tensile strength, notch tensile strength, Youngs modulus, and impact properties at temperatures down to 4 K (-454 F). The information presented here is based on a report by R. P. Reed and R. P. Mikesell "Low Temperature Mechanical Properties Of Copper and Selected Copper Alloys," NBS Monograph 101, Institute for Materials Research, National Bureau of Standards, Boulder, Colorado 80302.
Tests — The compositions and condition of these alloys — that is, for standard, commercially available mill stock — are listed in Table 1. Tensile specimens with 1.5 inch gauge lengths provided the data on elastic modulus. Notch tension (also 1.5 inch gauge lengths) and tension tests were conducted using the cryostat and related equipment. Tests were conducted at 295 (ambient), 195, 76, 20, and 4 K. An Instron testing machine was used with a crosshead speed of 0.02 in. per min. Test procedures are described by R.A. Warren and R.P. Reed in NBS Monograph 63.
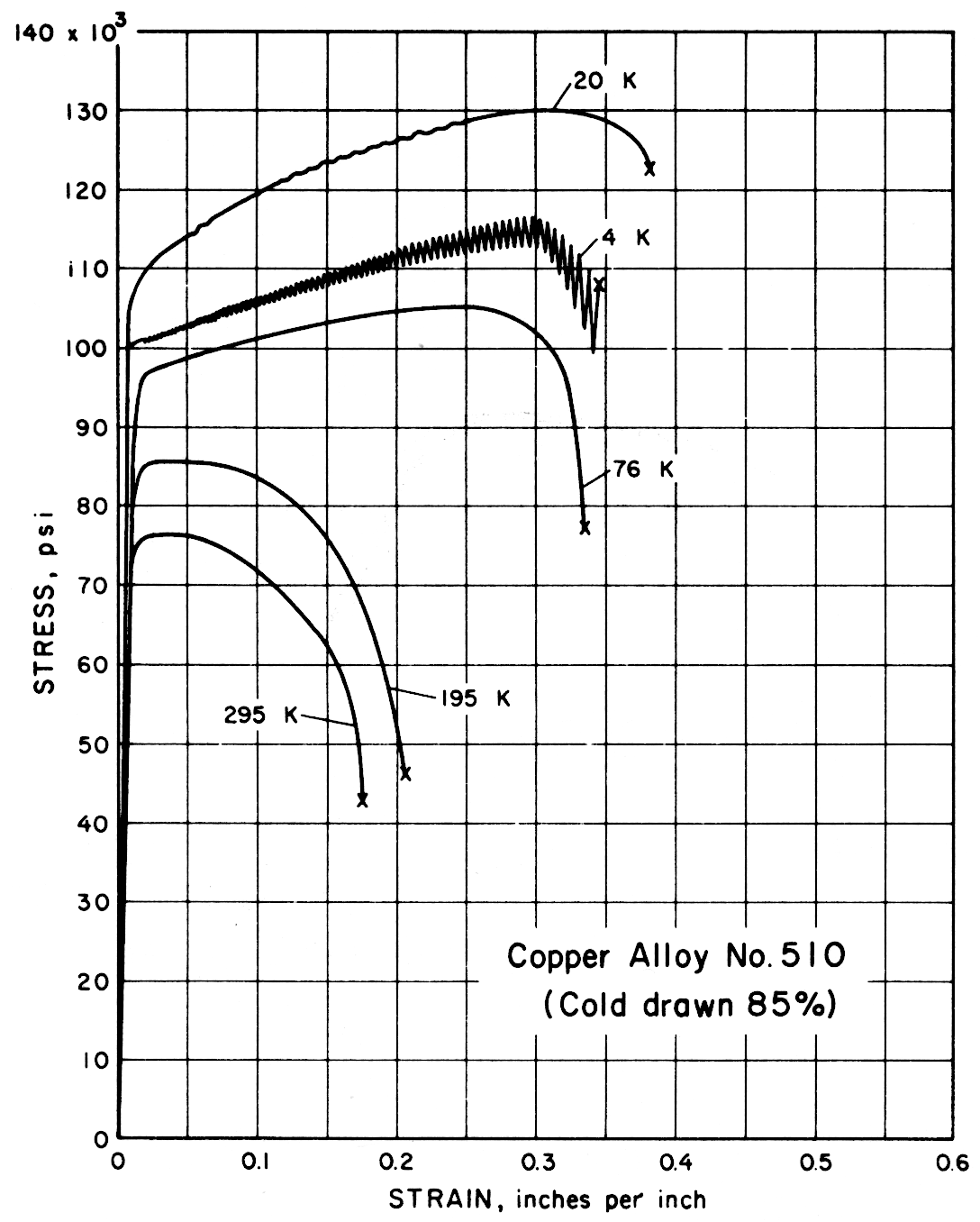
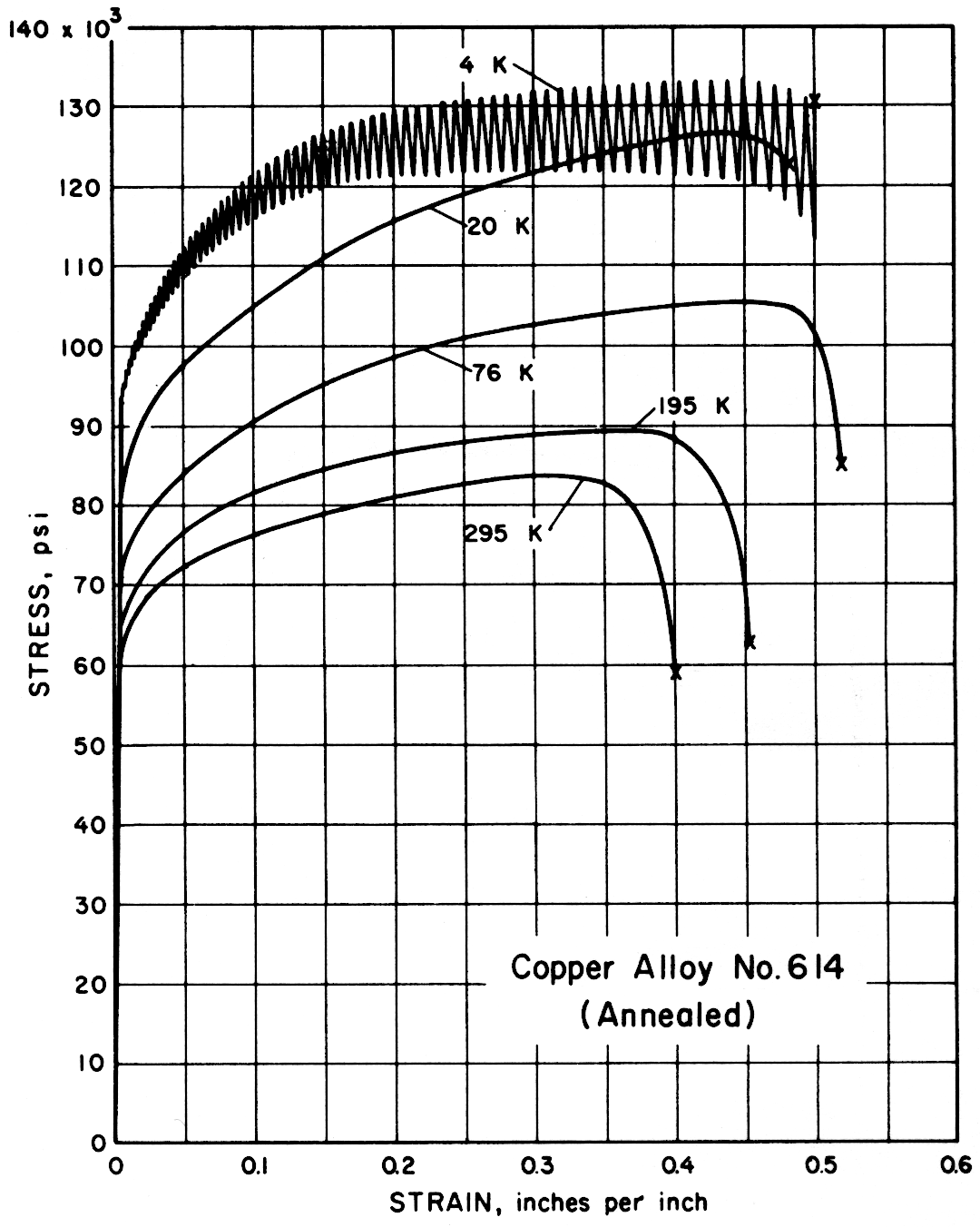
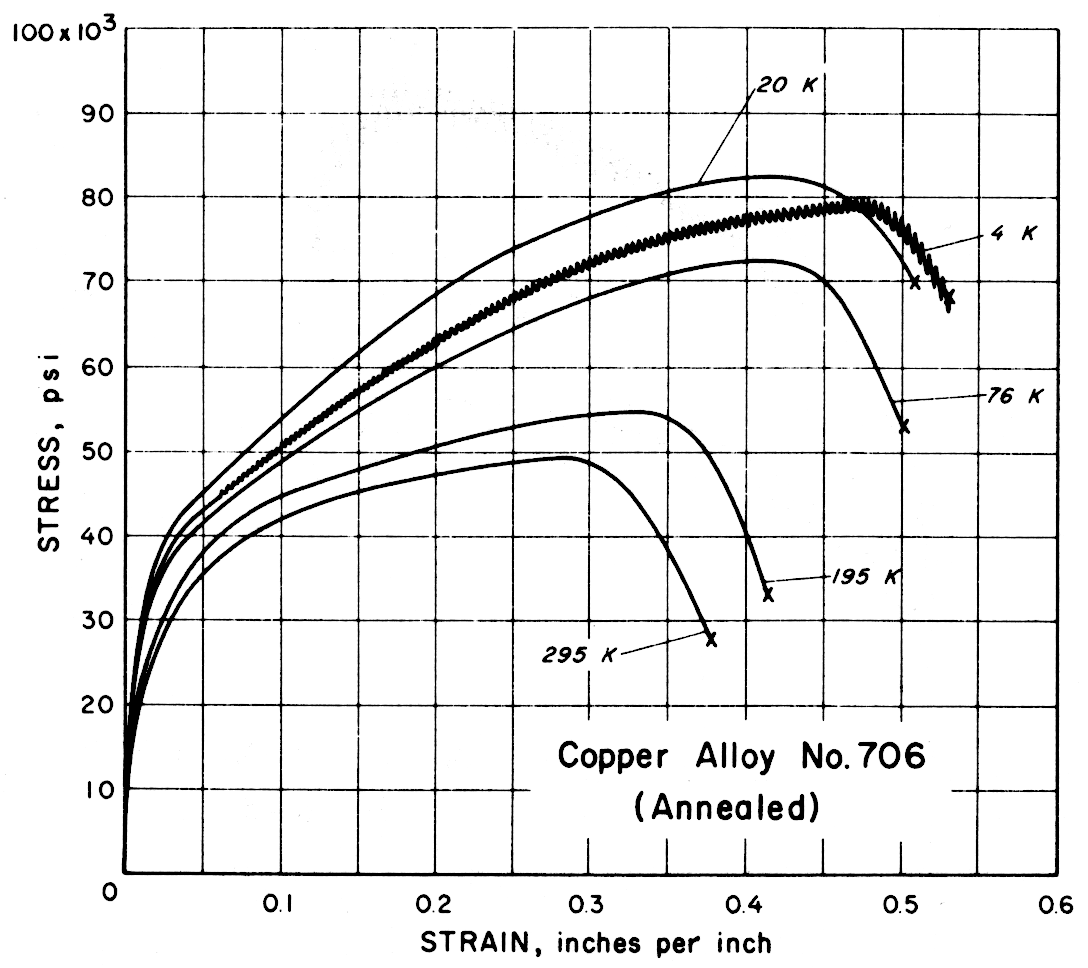
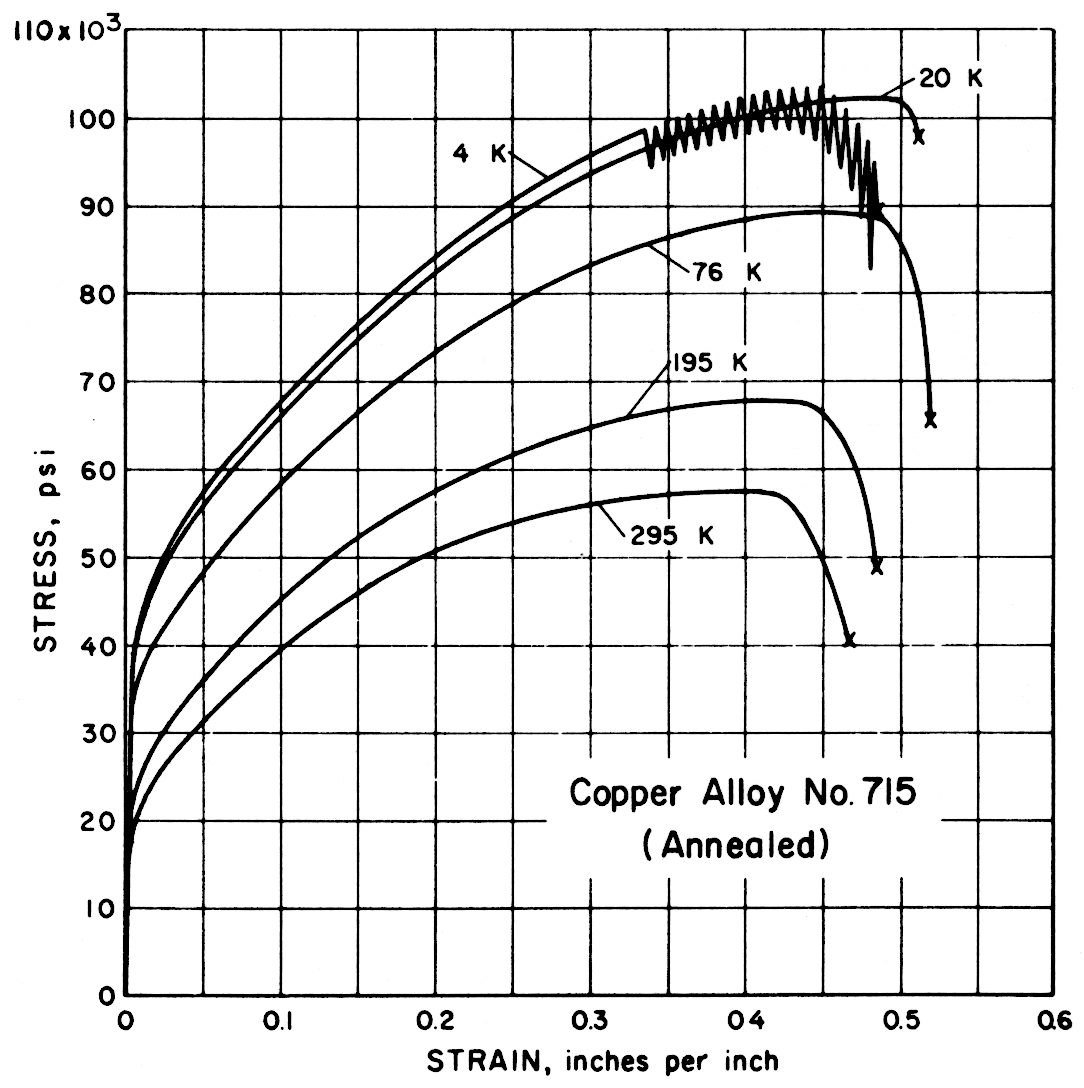
Results — The figures on the following pages present stress-strain behavior. In Table 2 the average data for each alloy are tabulated for all tests and temperatures. Data spread in most instances was less than ± 1%.
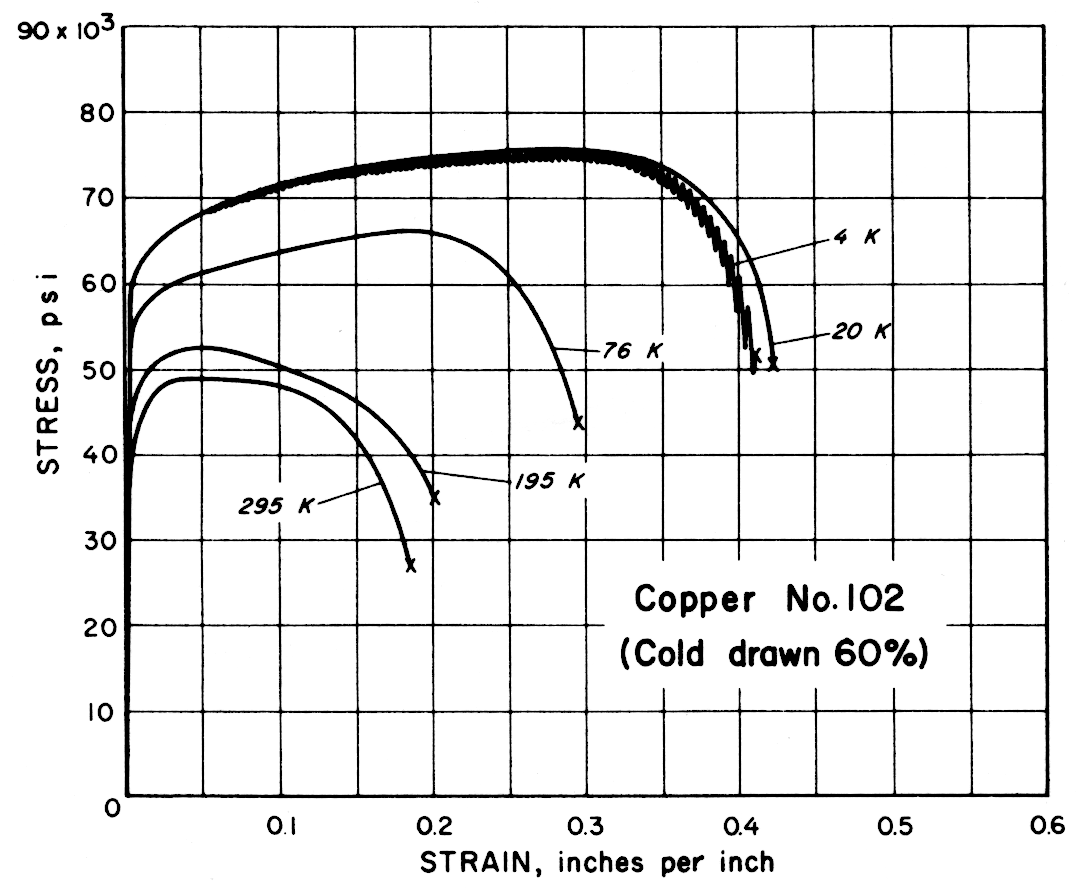
Considerable spread in the impact strength occurred for Copper 102 in the 60% cold-drawn condition. This was related to grain size. Metallographic examination revealed that the specimens with high impact strengths (113 to 115 ft-lb) had small grains while those with low impact strength (57 to 84 ft-lb) had large grains.
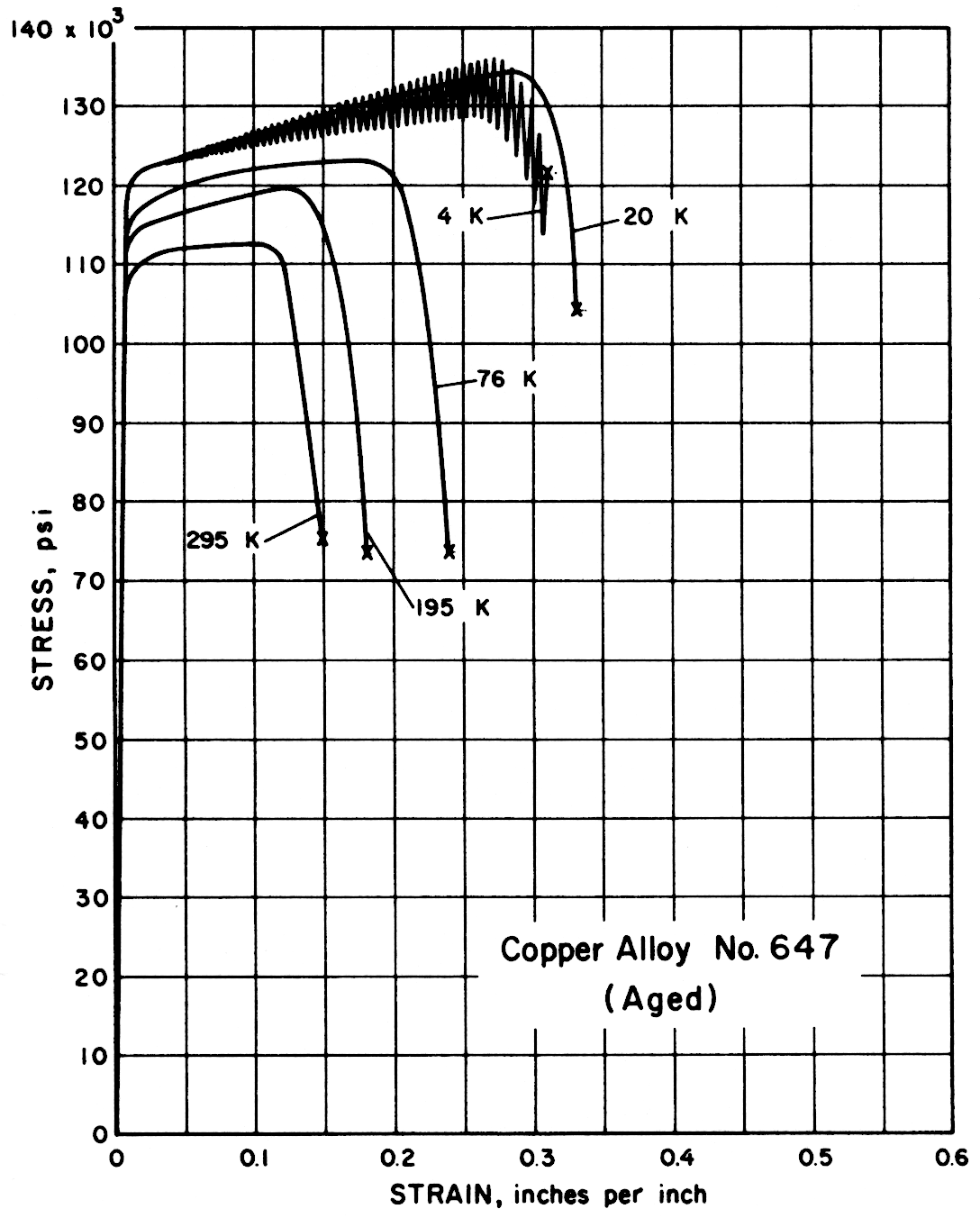
Aged Copper Alloy No. 647, although containing only about 2.5 wt. % alloying elements, proved to be considerably stronger than any other alloy tested. Its impact strength remains high, and the notch tensile strength, although falling off at 4 K, is good when compared to the tensile strength. In addition, elongation increases at low temperatures.
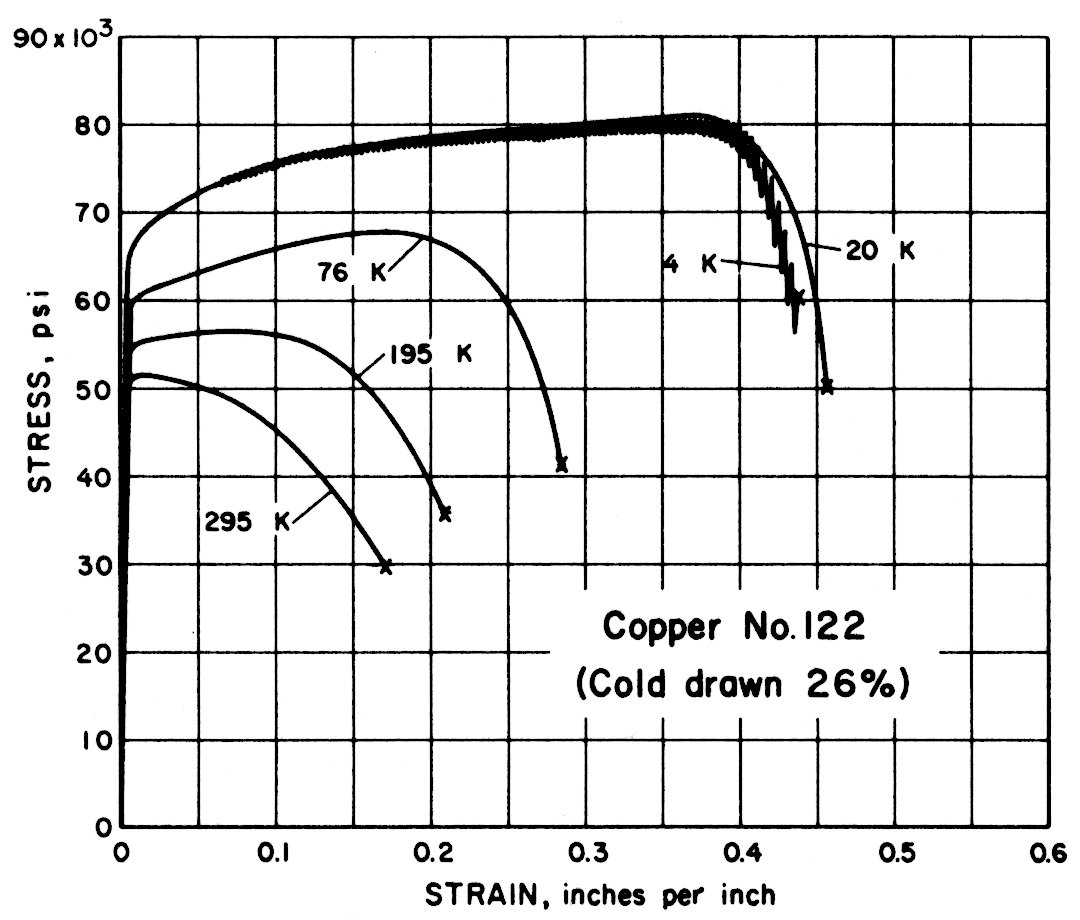
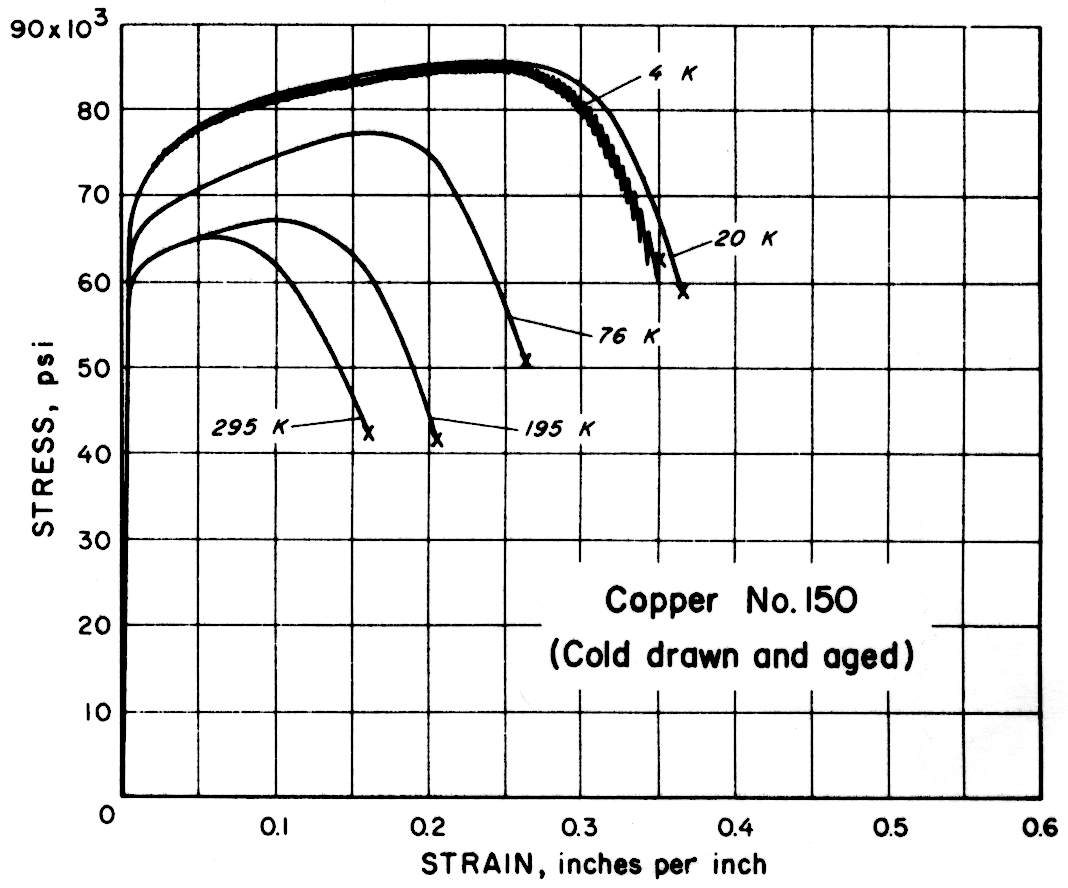
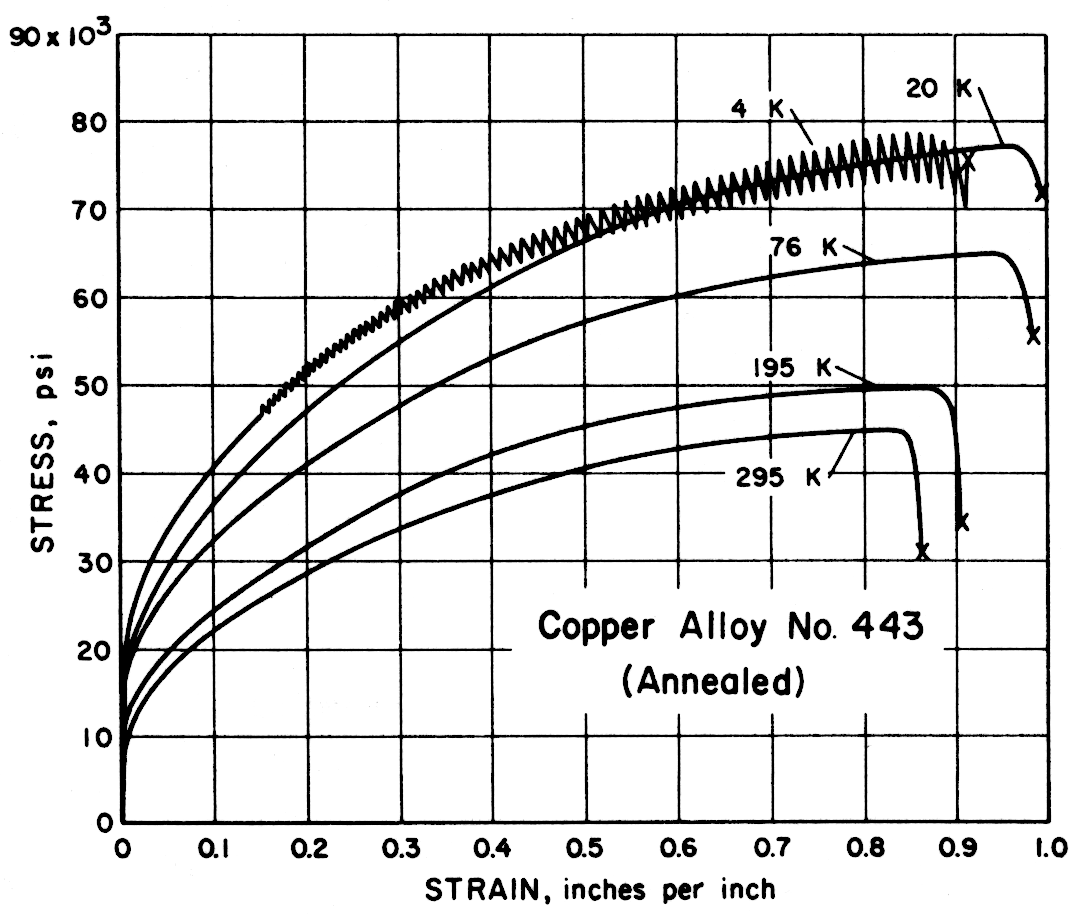
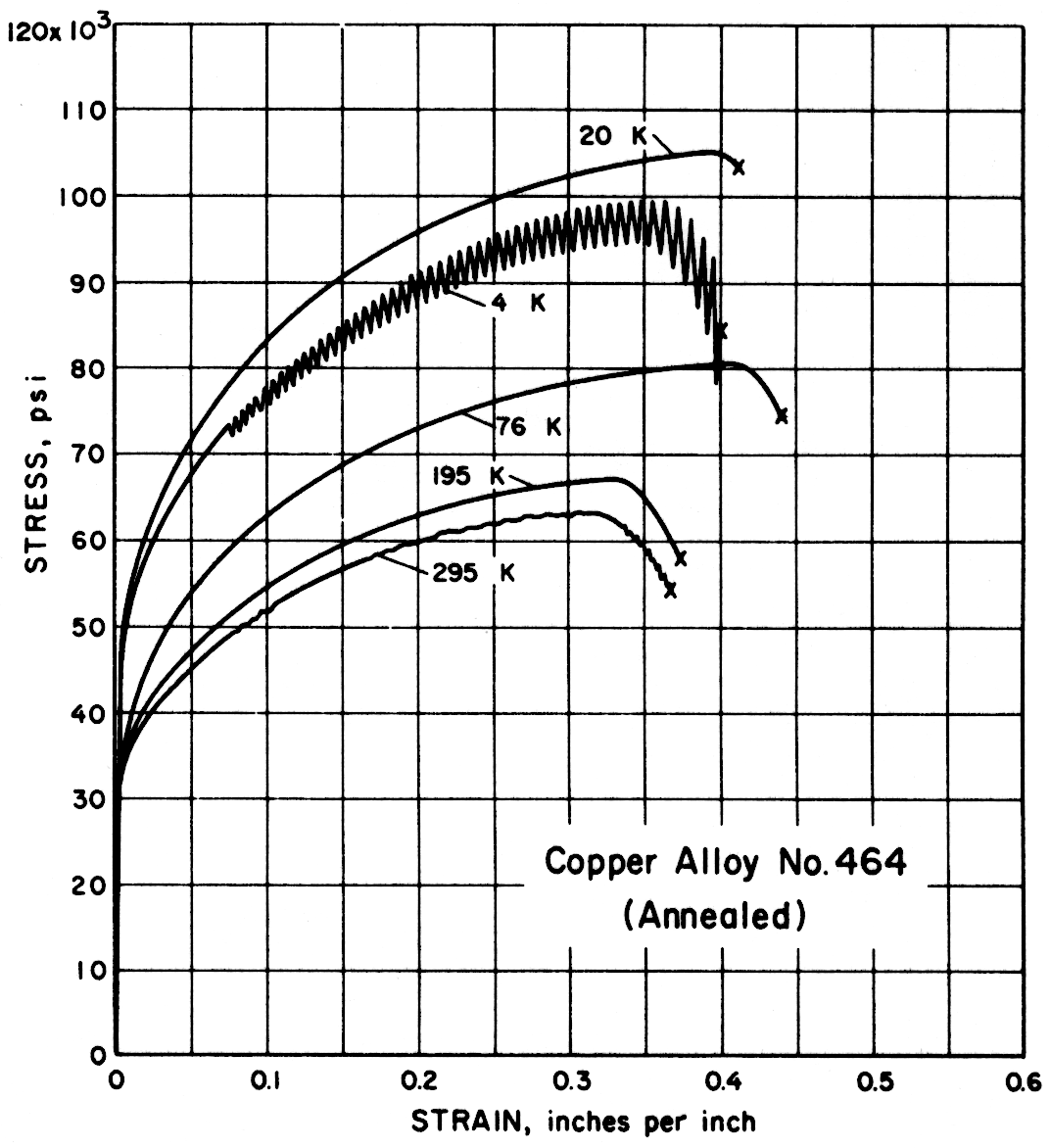
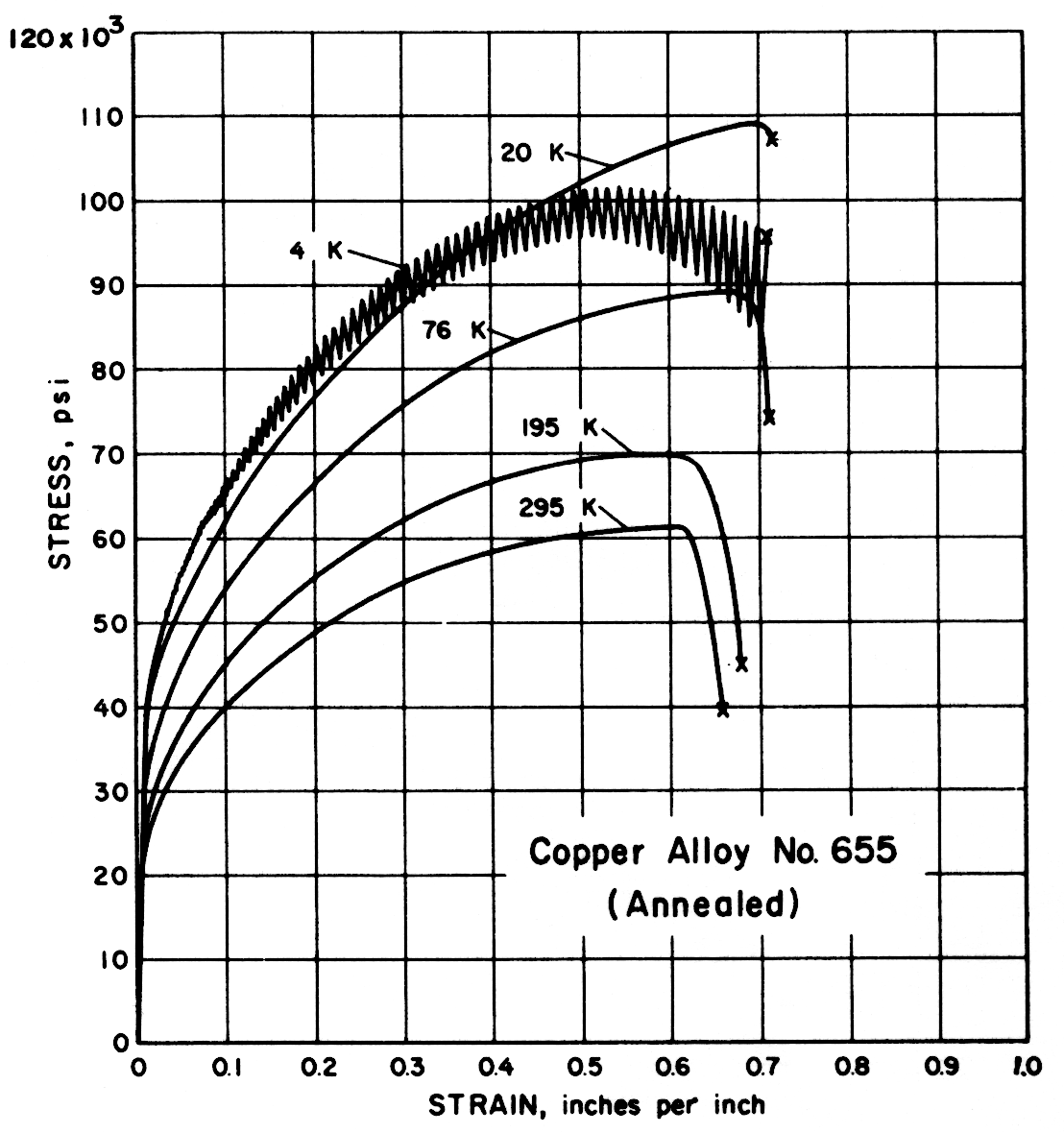
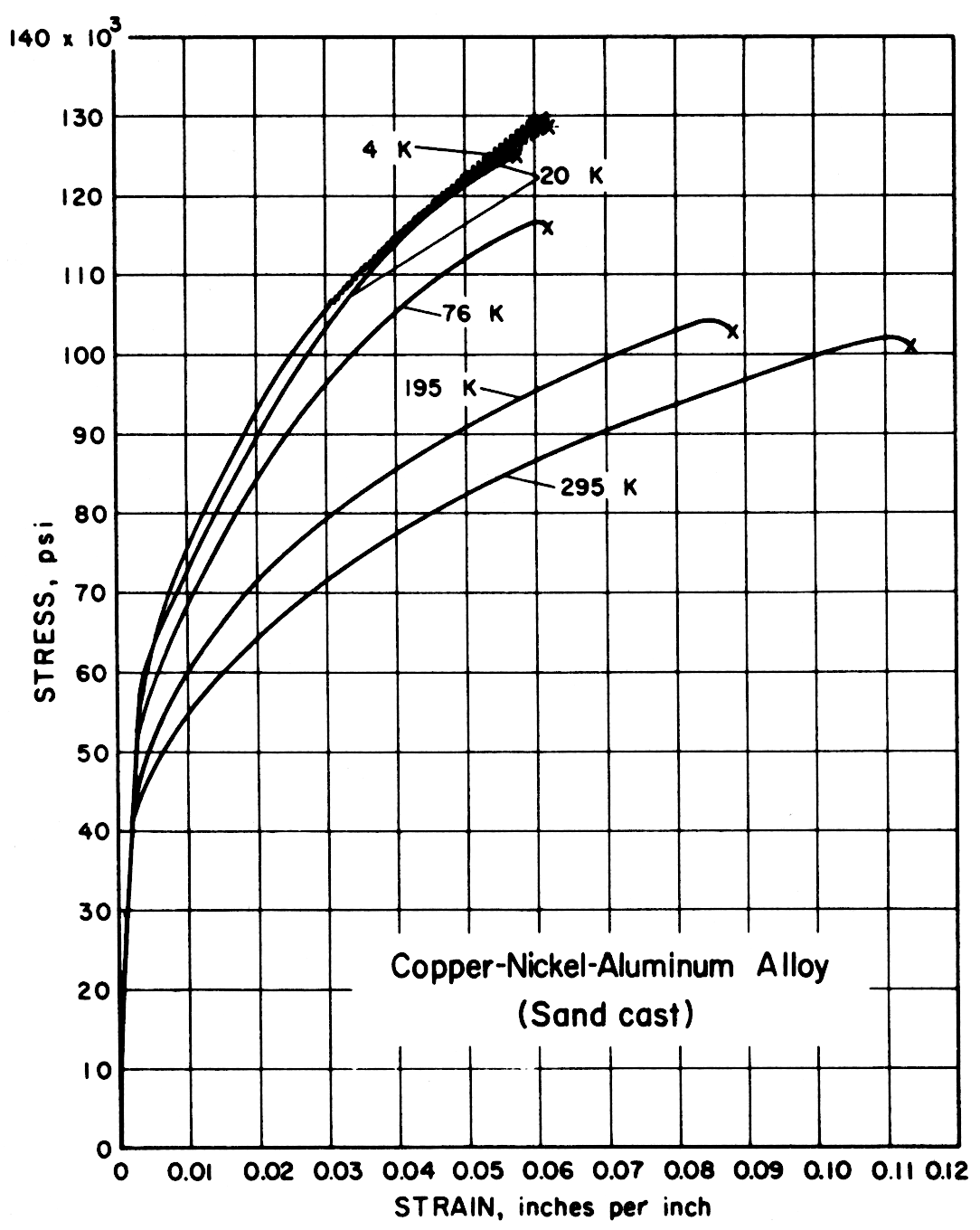
Except for the sand cast nickel-aluminum-bronze alloy, all alloys had notched-to-unnotched tensile ratios above one, and good or very good impact properties. Only the sand cast alloy was brittle at low temperature. For most alloys the tensile strength, yield strength, elongation and notch tensile strength increased in the temperature range from 295 to 20 K. Ultimate and yield strengths of most alloys are less at 4 K than at 20 K. Discontinuous yielding is evident in all stress-strain curves at 4 K.
Tables and Figures
| Copper and Copper Alloy* | Condition | Composition, % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Name | Pb | Fe | Sn | Zn | Ni | P | |
| 102 | Oxygen Free | Cold drawn 60% | 4 ppm | 4 ppm | 1 ppm | 4 ppm | 1 ppm | |
| 122 | Phosphorus Deoxidized, | Annealed | 0.0002 | 0.003 | 0.00035 | 0.001 | 0.028 | |
| High Residual Phosphorus | Cold drawn 26% | Same as annealed samples | ||||||
| 150 | Zirconium Copper | Annealed, 950 C; cold drawn 85 to 90%; aged, 450 C, 1 hr | Similar to that of Oxygen Free with Zr added | |||||
| 220 | Commercial Bronze, 90% | Annealed, 575 C, 3 hr | 0.005 | 0.01 | 10.01 | |||
| 230 | Red Brass, 85% | Cold drawn 14% | 0.02 | 15.33 | ||||
| 443 | Admiralty Arsenical | Annealed, 575 C, 1 hr | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 27.56 | ||
| 464 | Naval Brass | Annealed, 593 C, 1 hr | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.63 | 39.71 | ||
| 510 | Phosphor Bronze, 5% A | Spring cold drawn 85% | 0.02 | 0.02 | 4.85 | 0.05 | 0.18 | |
| 614 | Aluminum Bronze D | Commercial anneal | 2.13 | |||||
| 647 | Copper-nickel silicon | Aged, 450 C, 2 hr | 0.01 | 1.97 | ||||
| 655 | High Silicon Bronze A | Commercial anneal (soft) | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |||
| 706 | Copper Nickel 10% | Annealed, 677 C, 40 min | 0.02 | 1.16 | 0.07 | 9.98 | ||
| 715 | Copper Nickel 30% | Commercial anneal | < 0.01 | 0.59 | < 0.01 | 0.04 | 30.05 | |
| Nickel- aluminum bronze | Sand cast | 3.35 | 5.20 | |||||
| * Material was 3/4-in. bar, except nickel-aluminum bronze which was a billet. ** 16 ppm Ag; 12 ppm S; 2 ppm As; 5 ppm Sb; less than 3 ppm 0; traces of Au, Bi, Mn, Hg, Cd, Zn | ||||||||
| Copper and Copper Alloy* | Condition | Others | Hardness | Average Grain Diameter, mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Name | ||||
| 102 | Oxygen Free | Cold drawn 60% | ** | Rb 45 to 53 | 0.287 to 2.00 |
| 122 | Phosphorus Deoxidized, | Annealed | Ag, Bi, Sb, Mn, As, Ni (trace) | Rf 35 | 0.051 |
| High Residual Phosphorus | Cold drawn 26% | Rb 50 | 0.101 | ||
| 150 | Zirconium Copper | Annealed, 950 C; cold drawn 85 to 90%; aged, 450 C, 1 hr | Zr, 0.18 | Rb 68 | 0.203 |
| 220 | Commercial Bronze, 90% | Annealed, 575 C, 3 hr | Rf 49 | 0.051 | |
| 230 | Red Brass, 85% | Cold drawn 14% | Ag, Mg (trace) | Rf 64 | 0.025 |
| 443 | Admiralty Arsenical | Annealed, 575 C, 1 hr | As, 0.041 | Rf 55 | 0.144 |
| 464 | Naval Brass | Annealed, 593 C, 1 hr | Rb 57 | 0.036 | |
| 510 | Phosphor Bronze, 5% A | Spring cold drawn 85% | Rb 94 | 0.101 | |
| 614 | Aluminum Bronze D | Commercial anneal | Al, 6.57 | Rb 97 | 0.036 |
| 647 | Copper-nickel silicon | Aged, 450 C, 2 hr | Rb 98 | 0.025 | |
| 655 | High Silicon Bronze A | Commercial anneal (soft) | Mn, 0.88; Si, 2.90 | Rb 54 | 0.025 |
| 706 | Copper Nickel 10% | Annealed, 677 C, 40 min | Rb 33 | 0.051 | |
| 715 | Copper Nickel 30% | Commercial anneal | Mn, 0.71 to 0.73 Al, < 0.01; As, < 0.01 | Rb 47 | 0.036 |
| Nickel- aluminum bronze | Sand cast | Al, 9.95; Mn, 0.3 | Rb 93 | 0.036 | |
| * Material was 3/4-in. bar, except nickel-aluminum bronze which was a billet. ** 16 ppm Ag; 12 ppm S; 2 ppm As; 5 ppm Sb; less than 3 ppm 0; traces of Au, Bi, Mn, Hg, Cd, Zn | |||||
| Copper and Copper Alloy | Test Temperature, K | Elastic Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Name and Treatment | Youngs Modulus, 106 psi (5%) | Shear Modulus, 106 psi (2%) | |
| 102 | Oxygen Free (Cold drawn 60%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 17.3 20.0 22.0 | |
| 122 | Phosphorus Deoxidized, High Residual Phosphorus (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 15.1 16.0 16.2 16.3 16.4 | 6.46 6.81 7.20 7.44 |
| (Cold drawn 26%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 18.9 19.9 20.3 20.8 21.1 | ||
| 150 | Zirconium Copper (Cold drawn, aged) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 15.8 17.2 17.2 | |
| 220 | Commercial Bronze, 90% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 15.1 16.4 17.7 18.0 18.1 | 6.59 6.97 7.24 7.37 |
| 230 | Red Brass, 85% (Cold drawn 14%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 14.9 15.8 17.6 18.1 18.2 | 6.55 6.77 7.06 7.20 |
| 443 | Admiralty Arsenical (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 14.6 14.9 15.5 16.0 16.2 | 5.94 6.15 6.48 6.55 |
| 464 | Naval Brass (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 14.0 14.5 14.8 15.0 15.1 | 5.76 5.94 6.16 6.26 |
| 510 | Phosphor Bronze, 5% A (Cold drawn 85%, spring) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 15.6 16.5 16.7 16.5 16.4 | |
| 614 | Aluminum Bronze D (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 15.8 16.1 16.3 16.3 16.3 | |
| 647 | Copper-Nickel Silicon (Aged) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 21.4 22.3 23.2 23.5 23.6 | |
| 655 | High Silicon Bronze A (Annealed, soft) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 15.6 15.8 16.1 17.0 17.5 | |
| 706 | Copper Nickel 10% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 17.7 19.5 20.5 | |
| 715 | Copper Nickel 30% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 22.0 23.0 23.2 | |
| Nickel- Aluminum Bronze (Sand cast) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 16.8 17.8 18.5 18.5 18.5 | ||
| Copper and Copper Alloy | Test Temperature, K | Plastic Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uniaxial | ||||||
| No. | Name and Treatment | Tensile Strength, psi | Yield Strength, psi | Elongation, % in 4D | Reduction of Area, % | |
| 102 | Oxygen Free (Cold drawn 60%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 48,400 52,900 66,400 74,500 74,600 | 46,800 49,800 54,400 58,500 58,600 | 17 20 29 42 41 | 77 74 78 76 75 |
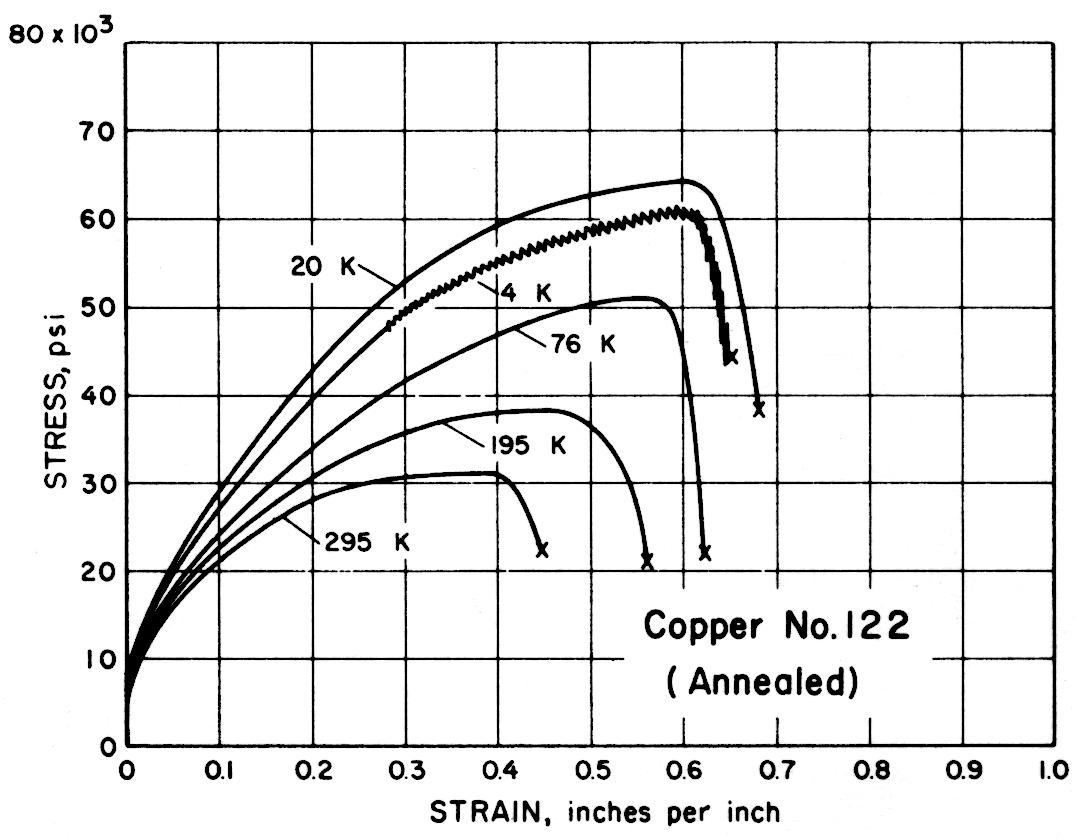
| 122 | Phosphorus Deoxidized, High Residual Phosphorus (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 31,300 38,300 50,600 63,800 60,400 | 6,700 6,600 7,400 8,400 7,900 | 45 56 62 68 65 | 76 87 84 83 81 |
| (Cold drawn 26%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 51,800 56,800 68,400 81,400 81,000 | 49,400 53,600 59,900 64,100 63,600 | 17 21 28 46 44 | 76 79 76 78 72 | |
| 150 | Zirconium Copper (Cold drawn, aged) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 64,450 67,200 77,400 85,200 85,700 | 59,600 61,300 65,700 66,400 64,700 | 16 20 26 37 36 | 62 66 71 72 69 |
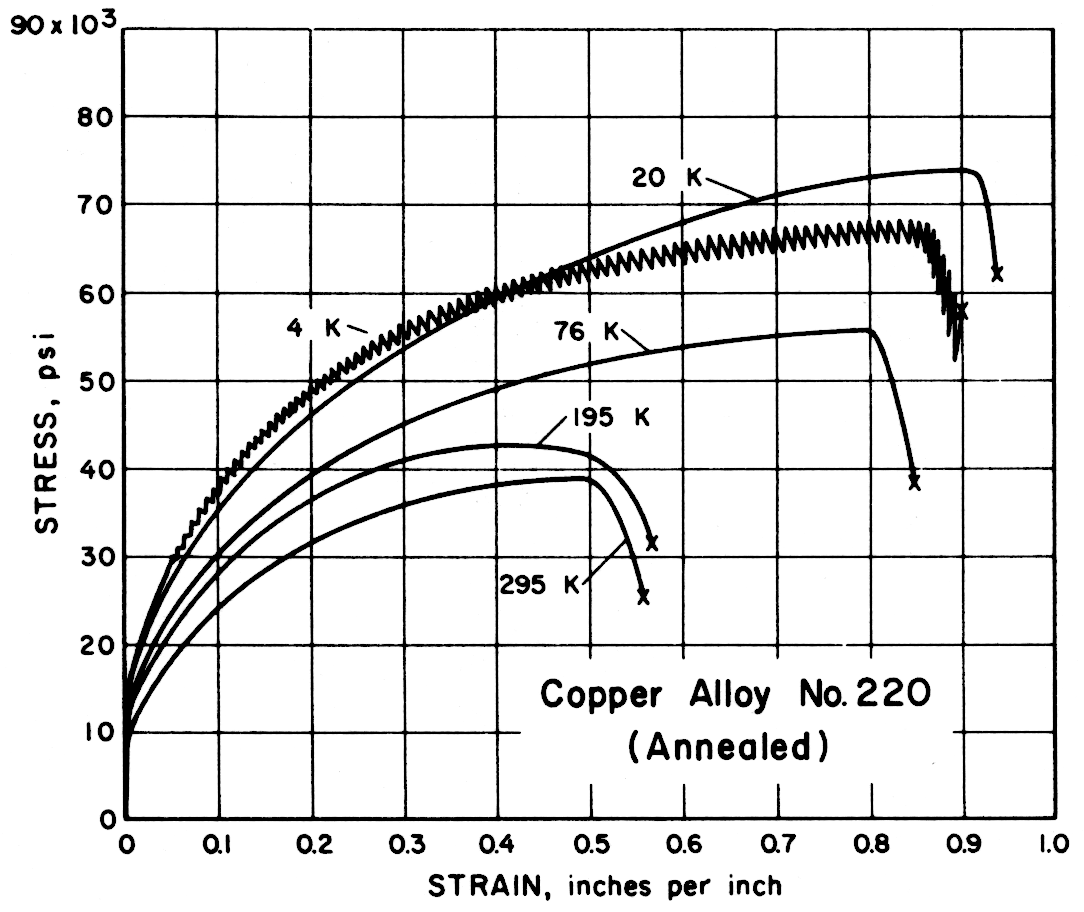
| 220 | Commercial Bronze, 90% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 38,500 41,800 55,200 73,200 68,200 | 9,600 10,200 13,200 15,600 15,000 | 56 57 86 95 91 | 84 80 78 73 73 |
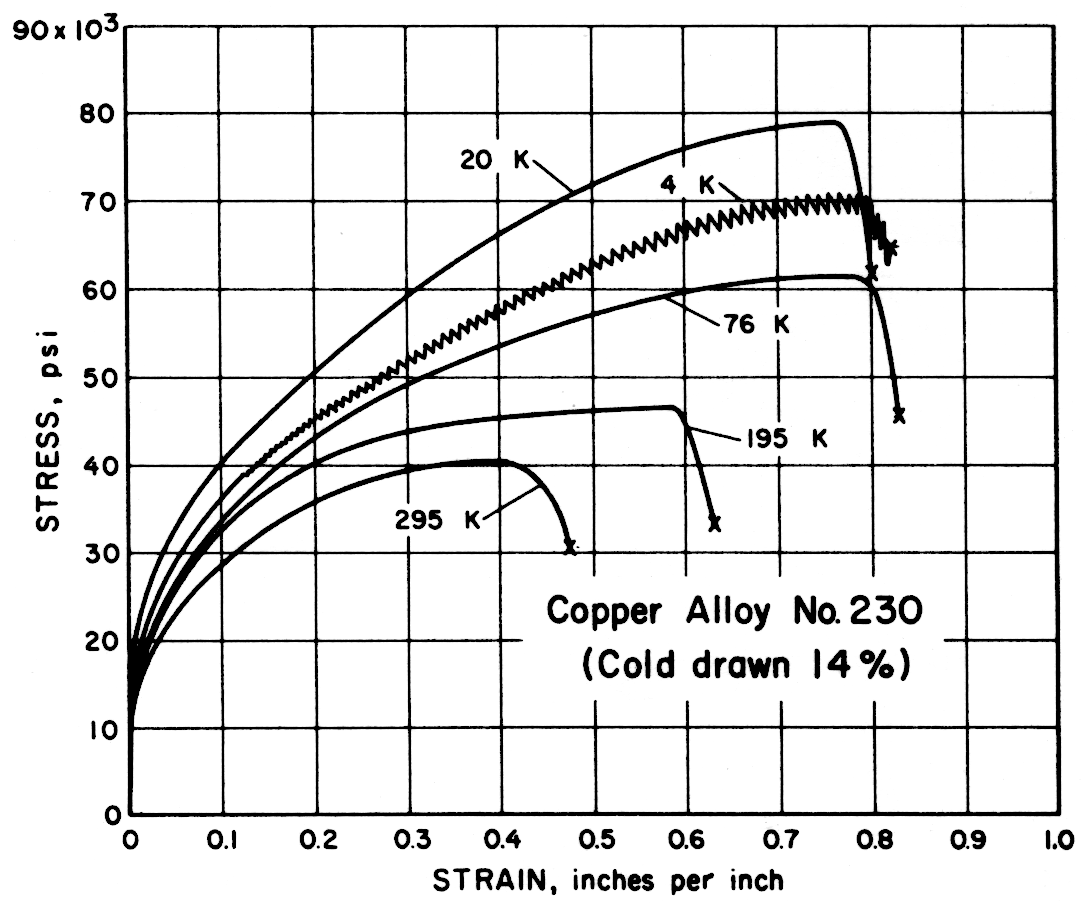
| 230 | Red Brass, 85% (Cold drawn 14%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 40,400 46,500 62,000 79,200 71,000 | 13,000 14,000 16,400 20,900 18,300 | 48 63 83 80 82 | 74 79 77 75 71 |
| 443 | Admiralty Arsenical (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 44,800 49,600 64,600 76,800 78,600 | 10,600 12,600 18,700 20,800 21,100 | 86 91 98 99 92 | 81 79 73 68 72 |
| 464 | Naval Brass (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 63,300 67,400 80,400 105,200 99,600 | 31,000 33,800 38,000 47,600 43,700 | 37 37 44 41 40 | 52 54 48 42 48 |
| 510 | Phosphor Bronze, 5% A (Cold drawn 85%, spring) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 77,400 85,600 105,200 131,000 116,400 | 72,000 78,700 89,200 104,800 100,400 | 18 20 34 39 34 | 78 78 67 62 58 |
| 614 | Aluminum Bronze D (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 83,200 89,500 105,800 126,400 134,500 | 59,400 64,800 69,500 80,600 82,400 | 40 45 52 48 52 | 66 71 64 58 59 |
| 647 | Copper-Nickel Silicon (Aged) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 112,400 119,400 123,600 133,700 135,800 | 105,000 110,800 114,100 118,400 119,800 | 15 18 24 33 31 | 60 66 70 68 65 |
| 655 | High Silicon Bronze A (Annealed, soft) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 61,400 69,900 89,000 108,900 101,200 | 24,200 26,800 31,900 37,600 36,900 | 66 68 71 72 71 | 79 79 69 69 70 |
| 706 | Copper Nickel 10% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 49,600 54,700 72,000 82,500 80,600 | 21,400 24,700 24,800 30,200 24,900 | 37 42 50 50 53 | 79 77 77 73 73 |
| 715 | Copper Nickel 30% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 57,800 68,000 89,800 103,100 104,600 | 18,700 22,200 31,600 38,100 40,100 | 47 48 52 51 48 | 68 70 70 66 65 |
| Nickel- Aluminum Bronze (Sand cast) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 101,200 104,600 117,100 126,600 130,500 | 44,000 47,800 54,900 61,600 60,100 | 11 9 6 6 6 | 9 9 7 2 5 | |
| Copper and Copper Alloy | Test Temperature, K | Plastic Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triaxial | ||||
| No. | Name and Treatment | Notch Tensile Strength (KT 5.0), psi | Impact Charpy Energy Absorbed, ft-lb | |
| 102 | Oxygen Free (Cold drawn 60%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 75,700 82,200 93,600 102,400 100,600 | 96 101 95 84 |
| 122 | Phosphorus Deoxidized, High Residual Phosphorus (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 43,300 50,400 62,300 72,000 74,700 | 11 112 112 118 |
| (Cold drawn 26%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 81,000 86,800 99,800 108,600 109,300 | 112 112 112 119 | |
| 150 | Zirconium Copper (Cold drawn, aged) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 97,600 103,100 112,400 119,000 121,600 | 89 105 114 114 |
| 220 | Commercial Bronze, 90% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 49,900 55,600 69,200 76,300 78,900 | 112 114 112 115 |
| 230 | Red Brass, 85% (Cold drawn 14%) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 53,900 58,500 71,200 72,000 74,900 | 96 82 78 76 |
| 443 | Admiralty Arsenical (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 53,800 58,800 75,200 89,400 86,200 | 112 113 114 114 |
| 464 | Naval Brass (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 74,700 84,800 100,700 113,900 115,400 | 38 42 38 35 |
| 510 | Phosphor Bronze, 5% A (Cold drawn 85%, spring) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 136,500 147,100 167,000 185,000 185,400 | 106 82 54 51 |
| 614 | Aluminum Bronze D (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 122,500 133,300 148,100 174,300 160,800 | 110 100 72 66 |
| 647 | Copper-Nickel Silicon (Aged) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 189,700 194,800 204,600 255,800 212,200 | 110 106 109 116 |
| 655 | High Silicon Bronze A (Annealed, soft) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 81,200 92,000 110,700 126,300 122,100 | 112 112 114 116 |
| 706 | Copper Nickel 10% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 65,000 73,100 87,200 96,800 100,000 | 114 113 115 116 |
| 715 | Copper Nickel 30% (Annealed) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 79,400 90,500 112,900 127,600 130,500 | 115 114 114 114 |
| Nickel- Aluminum Bronze (Sand cast) | 295 195 76 20 4 | 105,200 112,800 118,900 121,800 118,400 | 10 8 6 6 | |
Source: https://www.copper.org/resources/properties/144_8/